

V4641 Sagittarii
What is V4641 Sagittarii?
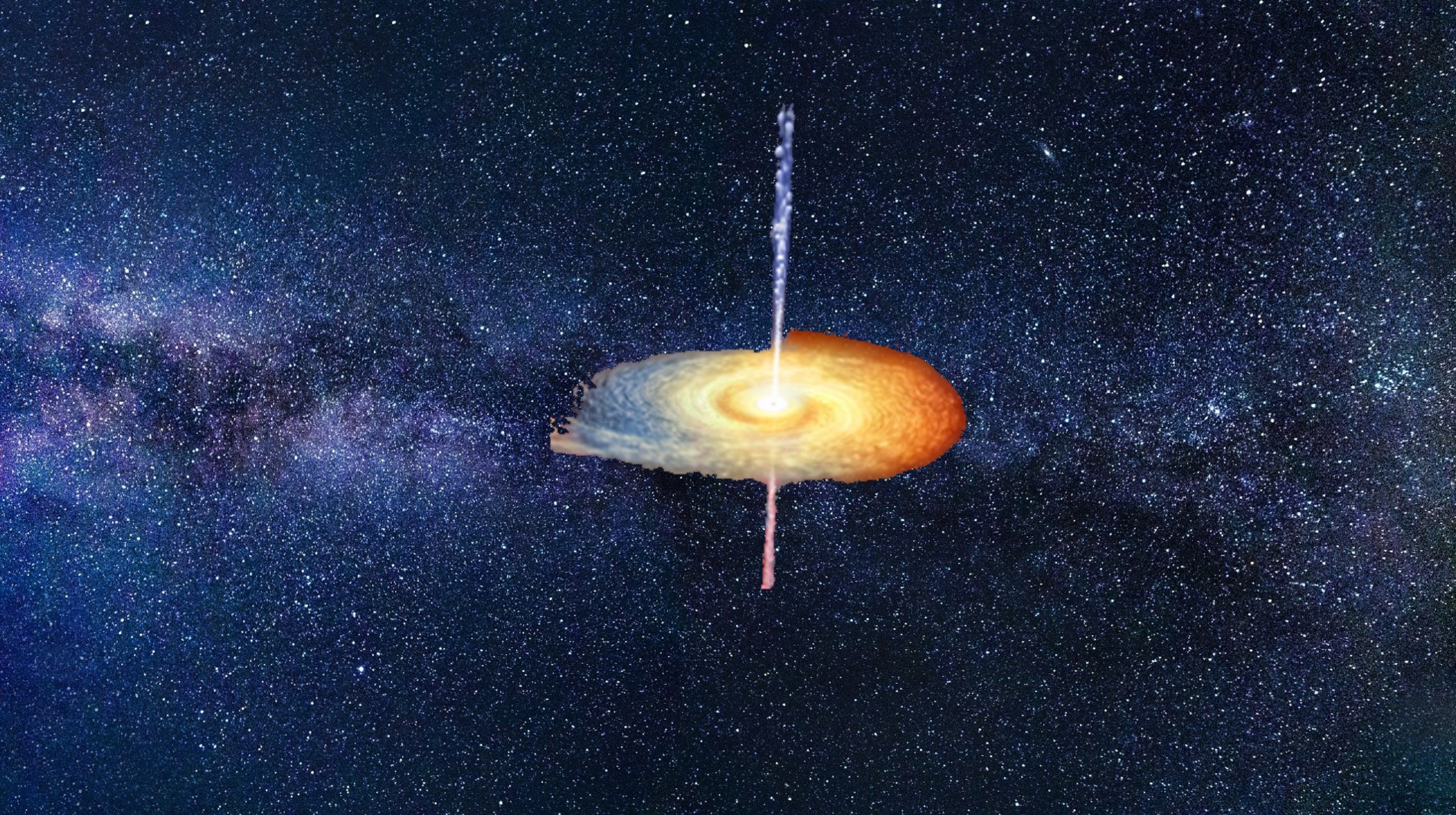
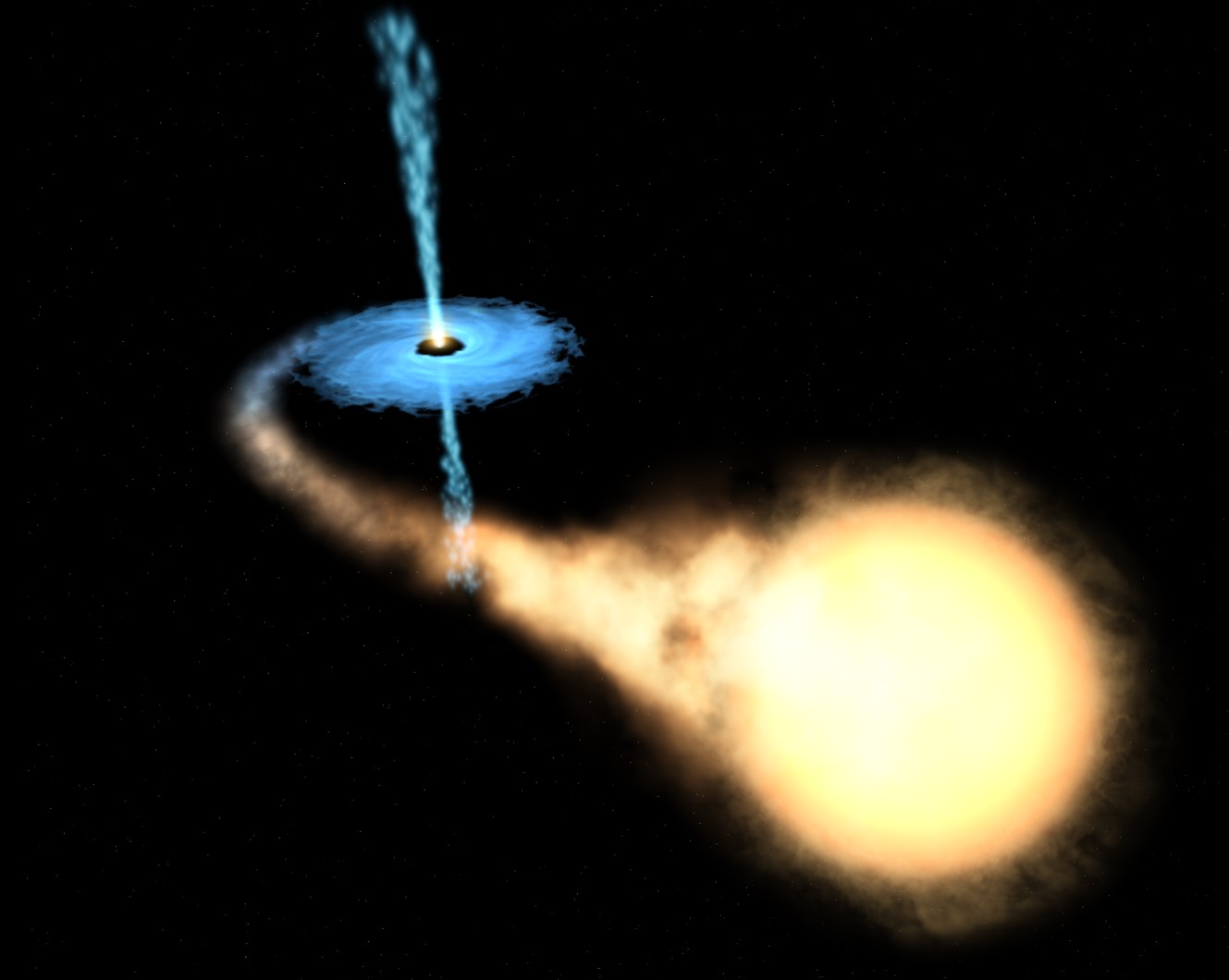
Located in the constellation Sagittarius, V4641 Sagittarii (also known as XTE J1819-254) is a fascinating variable X-ray binary star system, composed of a black hole and another star.
What is special about this black hole?
V4641 Sagittarii is home to the fastest superluminal jet ever discovered within the Milky Way. This extraordinary jet exhibits a phenomenon known as superluminal motion, where material is propelled away from the black hole at velocities exceeding the speed of light, although this apparent faster-than-light motion is actually due to the angle of observation. In addition, this black hole is currently engaged in a rare event called tidal disruption, during which it actively absorbs a nearby star. This phenomenon involves the immense gravitational forces of the black hole tearing apart the surrounding star, leading to the emission of intense bursts of X-rays and high-energy radiation.
Morphology
Geomorphology
Unfortunately, we do not know the dimensions of the black hole V4641 Sagittarii.
Anatomy
The resulting minimum mass of the compact object is estimated to be (6.4 ± 0.6) M☉. Additionally, astronomers have observed the presence of an accretion disk surrounding the black hole, but its composition remains a mystery, making it a subject of further investigation in understanding the anatomy of this intriguing black hole system.
Location
V4641 Sagittarii was initially identified as the potential nearest black hole to Earth, with an estimated distance of only 1,600 light-years. However, through continued observations of the system, astronomers have independently verified its distance to be several times that value, placing it at a minimum distance of approximately 24,000 light-years away from Earth. This black hole system is situated within the Milky Way galaxy, specifically in the constellation Sagittarius. The exact distance between the star and the black hole remains a subject of ongoing scientific investigation and exploration.
Physico-chemical properties
We do not know the composition of the accretion disk of this black hole.
Temperature
V4641 Sagittarii's accretion disk's temperature is unknown.
Age
Black hole V4641 Sagittarii's age is unknown.
Force fields
Gravitational force
There is no information about its gravitational pull.
Magnetic field
Its magnetic field is unknown to us.
Motions
Orbit
We don't know how long it takes to orbit the galaxy.
Rotation
We do not know its rotation time nor its speed.
Author: William Homier
Editor: William Homier
This page was last edited on 25 July 2023, at 17:00 (HAE).
Sources:

