

Earth
What is the Earth?
It is the third planet in our Solar System with a mass of 639 quatrillion tons and a diameter of 7917.51 miles (12874.75 kilometers). It is the only celestial body known whose atmosphere sustains life today.
Why is Earth a planet?
There are three things that define Earth as a planet: it orbits a star, it has a mass sufficient to overcome rigid body forces and it has taken on a shape that is nearly round.
Morphology

Geomorphology
Planet Earth ranks fifth in terms of size in our Solar System whose diameter is about 12,874.75 kilometers (8,000 miles) and has a surface dimension of 510,064,471.91 km² (196,936,993.248911 miles²). Due to its shape, Earth's circumference and diameter differ from that of a true sphere, that's why Earth is an oblate spheroid or ellipsoid.
Anatomy
Similar to other terrestrial planets, Earth's interior is divided into layers by its chemical or physical properties. In a nutshell, the outer layer is made of a chemically distinct silica crust, and then the mantle is made up of highly viscous solids at its base. We refer to the crust, upper mantle, and cold, rigid top of the earth's atmosphere collectively as the lithosphere, which is divided into tectonic plates that move independently. The density of the Earth is 5.51 g/cm³.
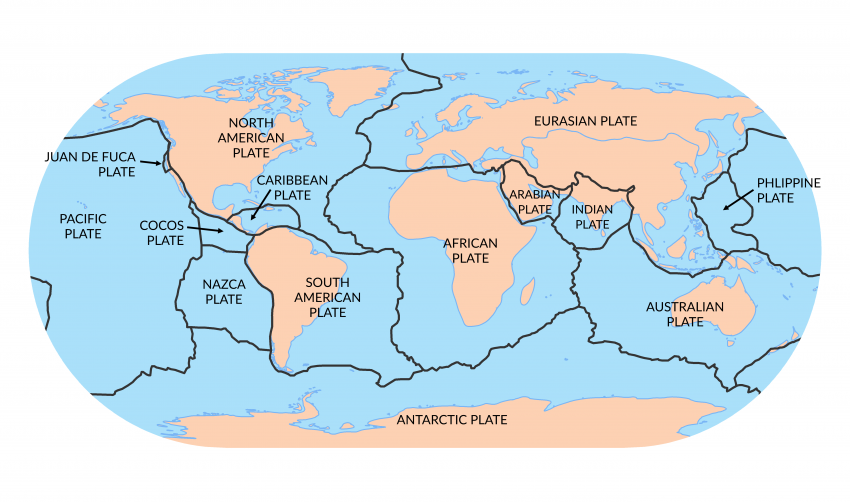
Tectonic plates
Tectonic plates are divisions of Earth's mechanically rigid outer layer, the lithosphere. There are three types of boundaries that these plates follow: convergent boundaries, divergent boundaries, and transform boundaries. At convergent boundaries, two plates come together, divergent boundaries, they are pulled apart, and transform boundaries, they slide past one another. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation can occur along these plate boundaries. Asthenosphere is the part of the upper mantle that is less viscous but solid enough to allow plates to move along with it.
Location
The Earth is approximately 93 million miles (149,668,992 kilometers) from the Sun (its hosting star).
Physico-chemical properties
Iron (32.1%), oxygen (30.1%), silicon (15.1%), magnesium (13.9%), sulfur (2.9%), nickel (1.8%), calcium (1.5%), and aluminum (1.4%) constitute the majority of Earth's mass, with the remainder consisting of trace amounts of other elements. It is estimated that the core region contains 88.8% iron, 5.8% nickel, 4.5% sulfur, and less than 1% trace elements, because of mass segregation.
Temperature
Potassium, uranium, and thorium are the most important elements that generate heat on Earth. As much as 6,000 °C (10,830 °F) may be present in the center of the Earth, the pressures can reach up to 360 GPa (52 million pounds of pressure). Scientists suggest that early in Earth's history, before short-lived radioactive isotopes were depleted, Earth's heat production was higher because much of the heat is provided by radioactive decay.
Age
Earth's age is about 4,543,000,000 terrestrial year.
Force fields
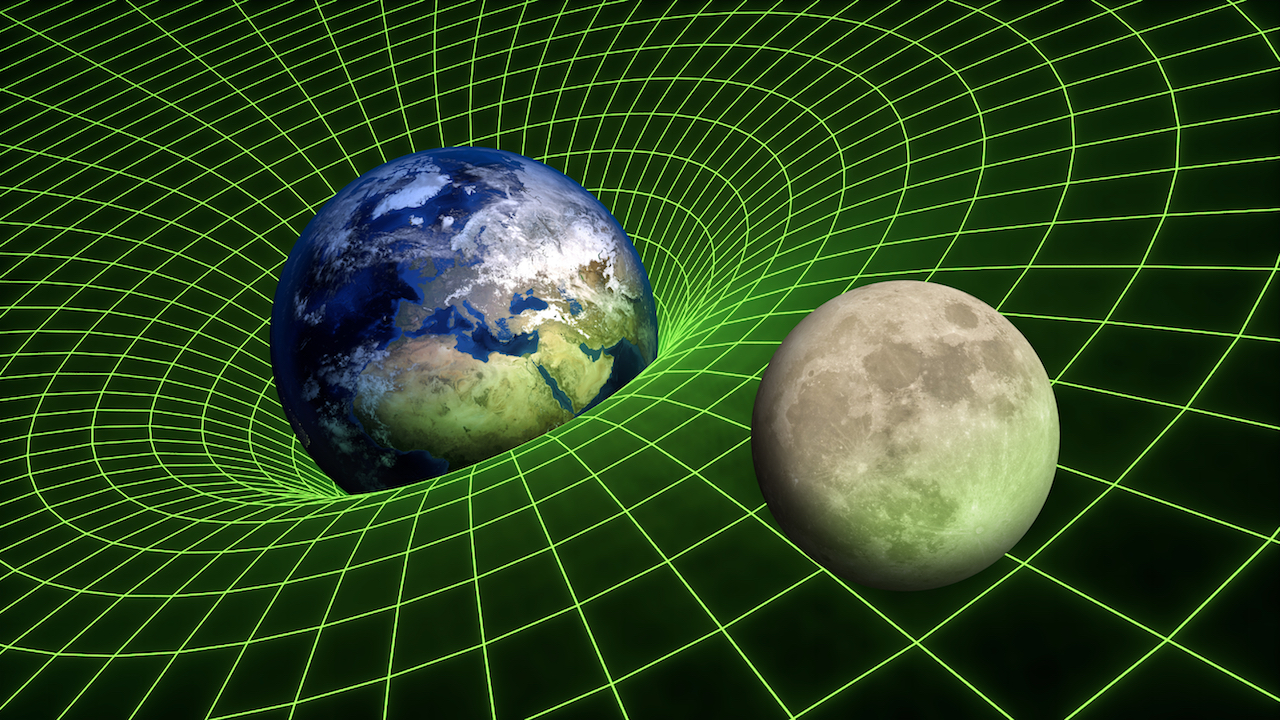

Gravitational force
Gravity refers to the acceleration imparted to objects by the distribution of mass on Earth. There are approximately 9.8 meters/second² (29 feet/second²) of gravitational acceleration at Earth's surface which is 1 gforce.
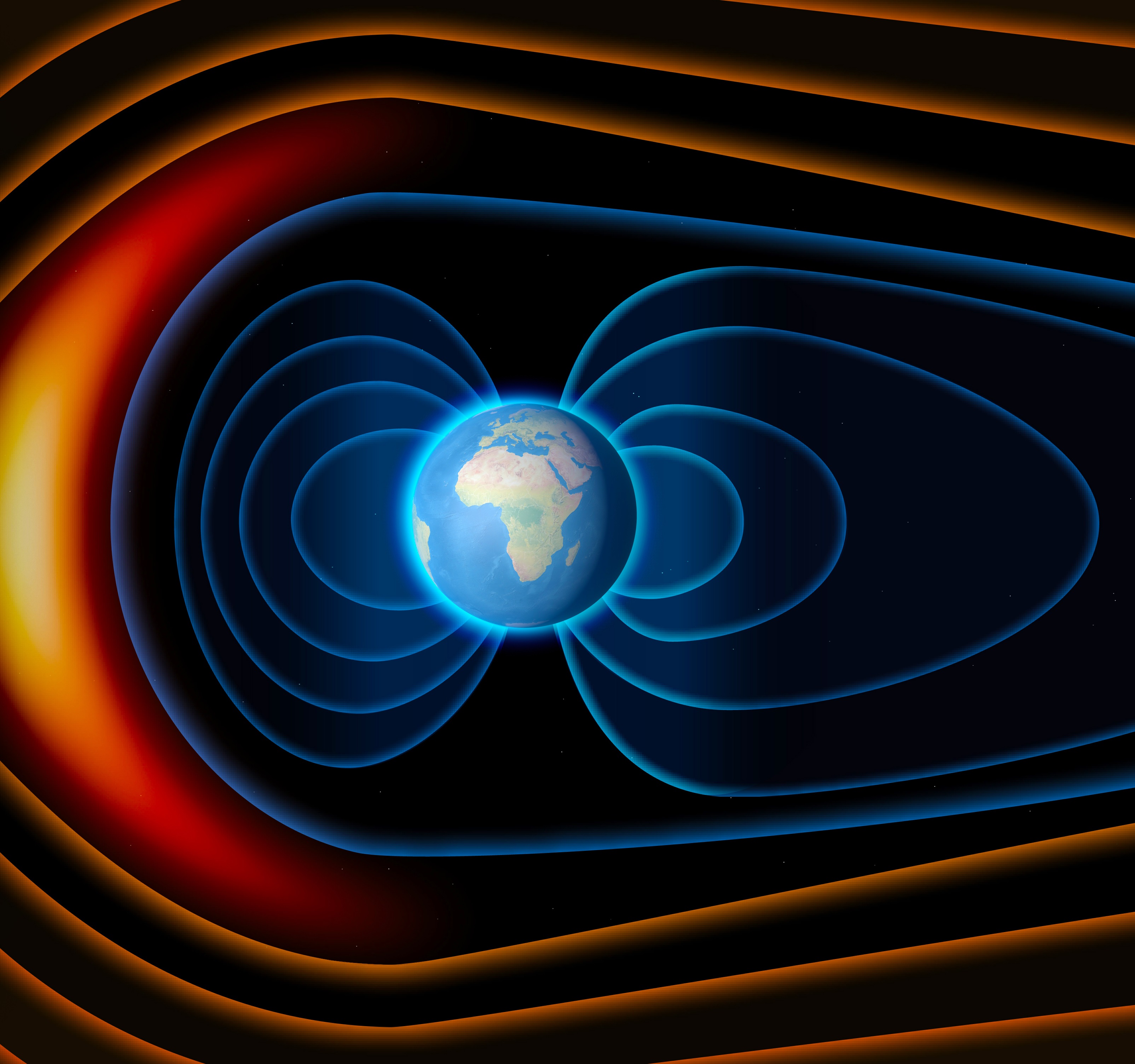
Magnetic field
Magnetic fields are generated by dynamos in the Earth's core, which converts energy generated by convection driven by thermal and compositional forces into electrical and magnetic field energy. A magnetic dipole moment of 7.79*1022 Am2 was measured at the equator of the magnetic field at epoch 2000, decreasing almost 6% per century at the equator of the magnetic field. Magnetic poles drift and periodically change alignment as a result of convection movement in the core. As a result, the main field has secular variation and field reversals at irregular intervals that average about once every million years. In the past 700,000 years, one such reversal was observed.
Motions

Orbit
It takes the Earth 365 days, 5 hours, 59 minutes and 16 seconds to orbit its hosting star "the Sun". The period of time it takes a planet to orbit its star is termed a year.
Rotation
A day is shorter in the past as the Earth rotates slower with time. Earth rotates once every about 24 hours depending on the Sun, but once every 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds depending on other distant stars.
Satellite systems

Moon system
As the only natural satellite of Earth, the Moon is also the fifth largest in the Solar System. and the largest satellite relative to its orbital planet.
Ring system
Earth does not possess a ring.
Author: William Homier
Editor: William Homier
This page was last edited on 11 April 2022, at 19:50 (HAE).
Sources:

