

Venus
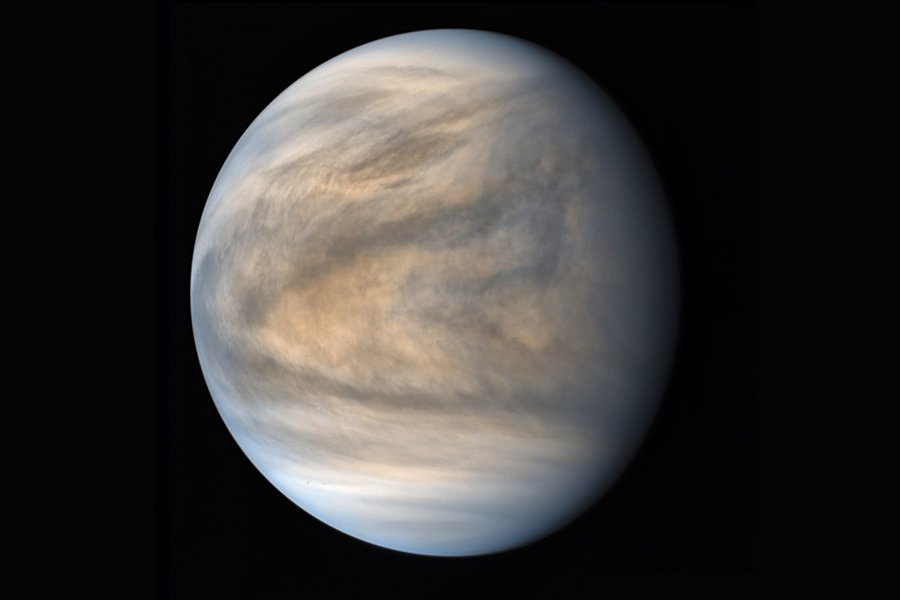

What is Venus?
Venus, the second planet closest to our Sun. The name of this planet derives from the Roman goddess of love and beauty. It is the second brightest natural object in Earth's night sky and during daylight hours after the Moon, and can cast shadows also.
What is special about Venus?
As opposed to our other solar system planets, Venus revolves on its axis clockwise. Likewise, it orbits the Sun anticlockwise, but its unusual axis rotation has to do with the fact that it was knocked off of its upright position in the past!
Morphology
Geomorphology
Approximately 12,104 km (7,521.0769 miles) in diameter, Venus covers 460,264,736.846 km² (177,709,208.070569 miles²).
Anatomy
As one of the rocky planets in the Solar System, Venus is one of the four terrestrial planets. In terms of size and mass, it is similar to Earth, thus it is often called its twin or "sister". The density of this planet is 5.24 g/cm³ and it has a mass of 4,867,000,000,000,000,000,000 tons.
Venus has a crust made up of smooth volcanic plains covering an area approximately 80% of its surface - 70% of which has wrinkle ridges and 10% of which has smooth or lobate plains.
There are two highland "continents" on Venus, one situated in its northern hemisphere, and the other just south of its equator. Known as Ishtar Terra after Ishtar, the Babylonian goddess of love, this northern continent is about the size of Australia. It is on Ishtar Terra that Maxwell Montes, the highest mountain on Venus, is located. The southern continent is known as Aphrodite Terra, after the Greek goddess of love, and is roughly as wide as South America (much of this area is covered by fractures and faults).
There are few impact craters on the surface, which indicates the planet is relatively young, having evolved within the last 300-600 million years.
The atmospheric pressure on Venus (about 95 bars) is 92 times that of Earth, this pressure is similar to the depth of about 1 km (0.6 mile) in Earth's oceans.
Tectonic plates
Location
The distance from the Sun to Venus is approximately 0.72 AU (107.53 million km or 66,816,044.3013 miles). Additionally, it is located approximately 54.783 million kilometers from Earth (486,844,329.118 miles).
Physico-chemical properties
In a similar manner to Earth, Venus is made up of a central core of iron and a rocky mantle. Almost all of its atmosphere is composed of carbon dioxide (96%), nitrogen (3%), and traces of sulfur dioxide is also present, the rest is still unknown.
Temperature
About 820° to nearly 900°F (437° to 482°C) appears to be the surface temperature of Venus, hot enough to melt lead and to evaporate nearly instantly water. This explains why the ocean basins are drier than usual.
Age
Venus' age is about 4,503,000,000 terrestrial year.
Force fields
Gravitational force
The surface gravity on Venus is 0.904488 gforce (8.87 m/s² or 29.10104 ft/s²) about 90.5% of the surface gravity on Earth, Since they both have almost the same size and mass.

Magnetic field
Venus is understood to not have a magnetic field of force. The explanation for its absence is partly due to its slow rotation (243 days) and its predicted lack of an internal thermal convection, any liquid metallic portion of its core couldn't be rotating fast enough to get a measurable global force field. Venus only has an induced a magnetosphere formed by the Sun's flux carried by the solar radiation.
Motions

Orbit
Every 224.7 terrestrial days, Venus completes one orbit around the Sun. Its orbit is currently the closest to be circular, with an eccentricity of less than 0.01. Based on simulations of early solar system orbital dynamics, Venus' eccentricity may have been significantly higher in the past, reaching values of 0.31.
Rotation
Venusian days are approximately 243 terrestrial days long.
Satellite systems
Moon system
Venus does not have any moons.
Ring system
Venus is ringless.
Author: William Homier
Editor: William Homier
Sound credit goes to GALAXIAN HD.
This page was last edited on 11 April 2022, at 19:50 (HAE).
Sources:

